What is Roasting in Cooking?
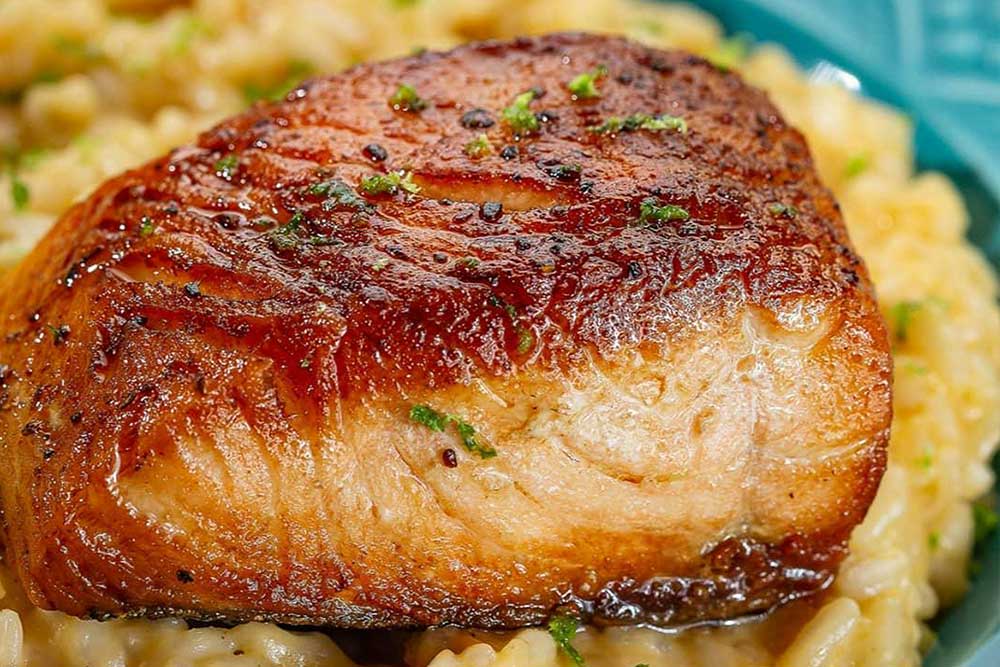
Roasting is a cooking method that involves cooking food in an oven or over an open flame. It is traditionally a dry-heat cooking technique for larger cuts of meat, poultry, and vegetables. The process involves exposing the food to direct heat. The heat is usually applied from all sides, resulting in a caramelization of the surface and a flavorful, browned exterior.
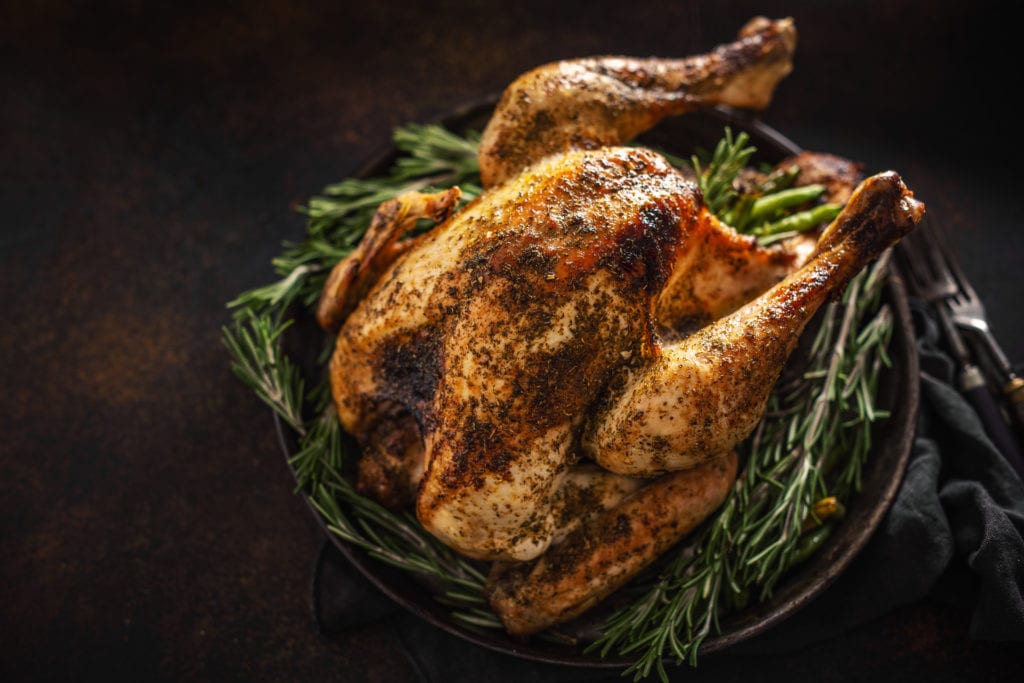

Roasting in Cooking with CVap Cook and Hold Ovens
CVap® ovens were initially designed as roasting ovens (though they have come a long way since their inception). Consequently, CVap ovens are perfect for roasting. The CVap advantage is that cooking takes place below the temperature of collagen shrink. Those tough connective collagen fibers contract at higher temperatures, but low, slow cooking in a CVap oven dissolves them, making even the toughest cuts tender. This makes it possible to get the desirable effects of roasting without the collagen shrink that squeeze juices out of meats. CVap technology maintains juiciness, making the results succulent, tender, and delicious.
How Does Roasting Work?
Temperature: Roasting is traditionally done at higher temperatures, typically ranging from 300°F (150°C) to 450°F (230°C) or even higher. The high temperature helps create a crisp and golden exterior while sealing in the food’s juices.
CVap ovens are inherently different. Rather than blasting away with high temperatures, CVap ovens cook at relatively low temperatures (maxing out at around 200°F (93°C) vapor temperature and 350°F (177°C) air temperature. CVap ovens utilize a dual air/vapor heat system to achieve the ideal aesthetics one expects from traditional roasting, with the added benefits of incredible tenderness and better yields.
Caramelization and Maillard Reaction: As the food is exposed to heat, the surface undergoes caramelization and the Maillard reaction. Caramelization involves the browning of sugars, while the Maillard reaction is a complex chemical process that results in the browning of proteins and the development of rich flavors and aromas.
Internal Temperature: It’s essential to monitor the internal temperature of the food, especially for larger cuts of meat. A meat thermometer helps ensure the food reaches a safe internal temperature while avoiding overcooking. Of course, in CVap ovens, overcooking is virtually eliminated. Series 7 CVap ovens allow you to utilize an optional food probe, making perfect roasting even more foolproof.
There are guidelines for different kinds of foods. An excellent source for safe doneness temperatures can be found on the foodsafety.gov website.
What Can You Roast in a Cook and Hold Oven?
Here’s a broad list of foods you can roast in a CVap Cook and Hold Oven.
BEEF
- Ribs
- Brisket
- Corned Beef
- Hamburgers
- Loin, Sirloin Butt
- Meatloaf
- Portions Filet
- Rib, Ribeye
- Rib, Roast-Ready
- Round
- Round, Rump (Steamship)
- Sirloin, Top
- Tenderloin

CHICKEN
- Breast, Boneless
- Halves
- Legs/Thighs, Quartered
- Whole

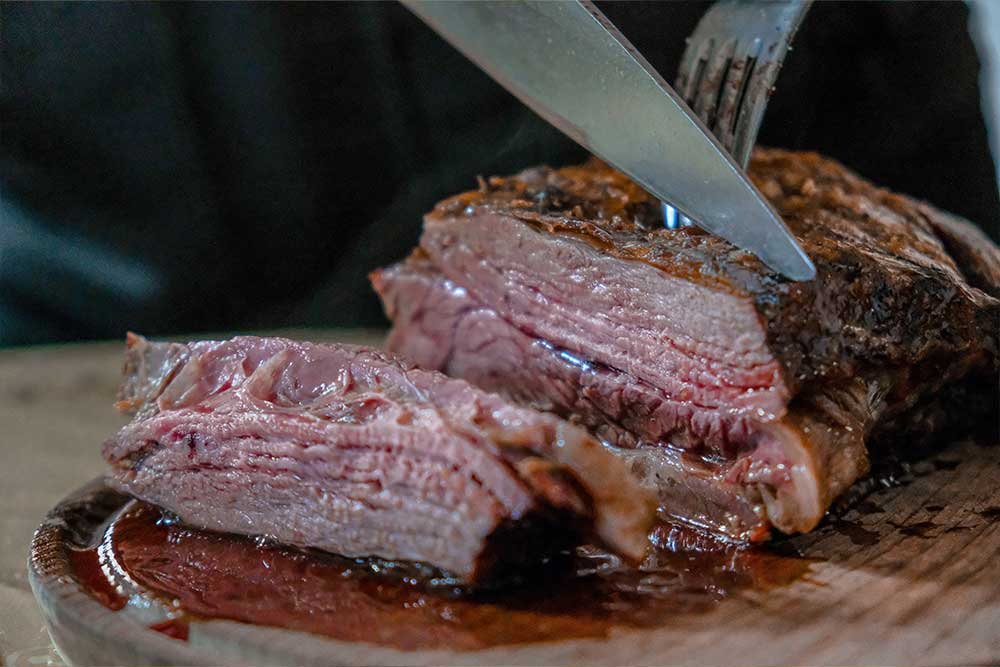
LAMB
- Leg
- Rack, Ribeye
- Ribs
- Shoulder
- Sirloin

VEAL
- Chuck
- Hotel Rack
- Legs
- Loin
- Rack, Ribeye
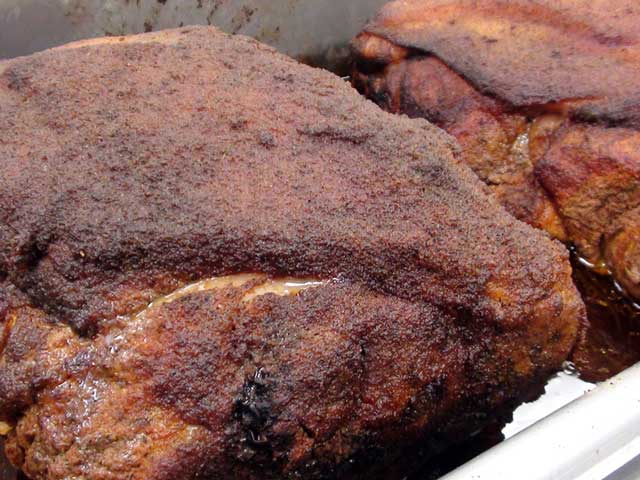

PORK
- Bacon, Sliced
- Leg, Fresh Ham, Inside
- Loin
- Pork Chops
- Pork Ribs – Back, Spare, St. Louis
- Roasting Pig, Suckling
- Shoulder, Boston Butt
- Shoulder, Picnic
- Sausage, Links, or Patties
- Tenderloin
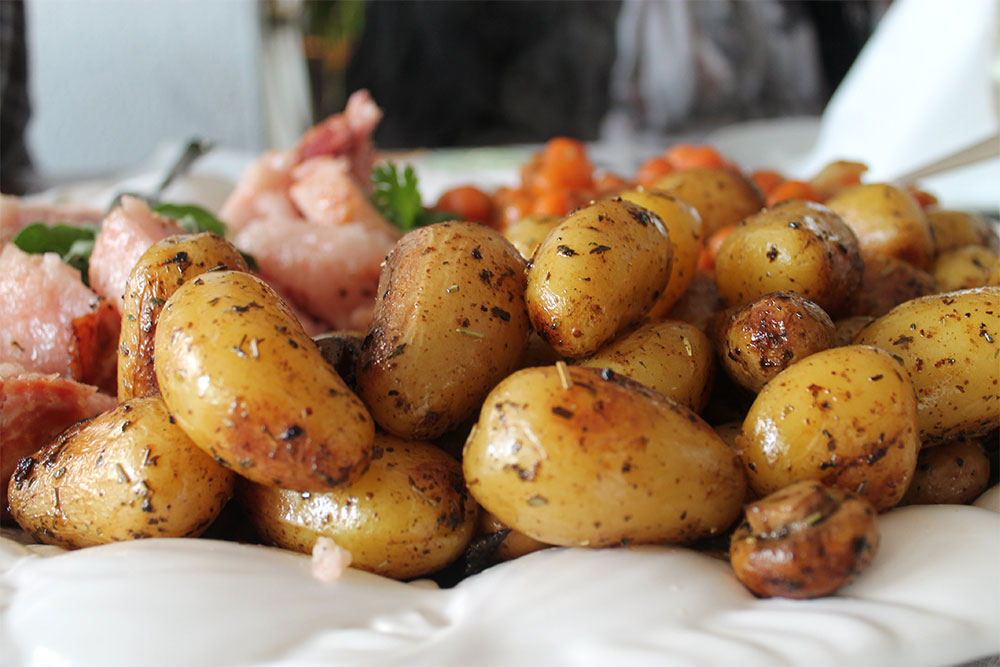

POTATOES
- Halved / Quartered
- New, Whole
- Quartered
- Whole 60-90ct.
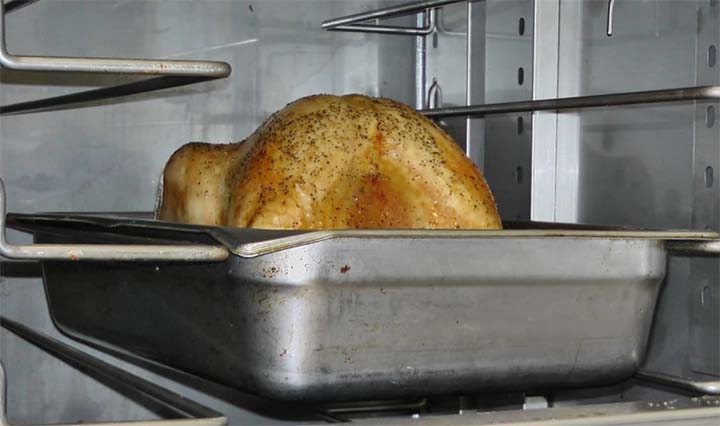

TURKEY
- Legs/Thighs, Quartered
- Roast, Boneless
- Whole

SEAFOOD
- Fish, Portioned
- Fish, Whole (1-2 lbs.)
When using a CVap Cook and Hold Oven, it’s essential to follow specific guidelines, as the extended cooking times and low temperatures vary depending on the type of food you’re preparing. For precise recommended settings, check out our cook and hold guidelines.

Advantages of Roasting in Cooking
Increased Yield: CVap ovens, with their dual heat system, deliver yields that blow the competition away. Better yields mean more servings per roast and more money in your pocket.
Flavor Enhancement: Roasting intensifies the natural flavors of ingredients. The heat caramelizes sugars and browns proteins, creating a rich and complex flavor profile. This is especially true for vegetables and meats.
Maillard Reaction: The Maillard reaction occurs when proteins and sugars in food react at high temperatures, resulting in the browning of the outer layer. This reaction adds depth of flavor, enhances aroma, and contributes to the appealing appearance of the roasted food.
Texture: Roasting can create a pleasing contrast in texture. Meat often develops a crispy and flavorful exterior while maintaining a juicy and tender interior. Vegetables can caramelize on the outside while retaining a firm texture inside. CVap ovens allow you to select the precise texture you desire.
Versatility: Roasting is a versatile technique applicable to a wide range of ingredients, including meats, poultry, fish, vegetables, and even fruits. It allows for creative combinations and experimentation with different flavors and textures.
Uniform Cooking: Roasting provides heat distribution, ensuring that food cooks uniformly. This is particularly beneficial for large cuts of meat or when roasting multiple items simultaneously. CVap ovens stand out in their ability to cook uniformly.

