When considering food holding cabinets, it’s important to understand that they are not all the same, falling into three basic categories: dry, passive humidified, and humidified. The “Dry vs. Humidified Cabinets” distinction is crucial, with significant differences in how they control temperature, humidity, food quality, and overall operational benefits.
Here’s a detailed comparison:

Dry Cabinets
Description: Dry cabinets are the most basic type, often referred to as “hot boxes.” They are essentially simple metal boxes with heating elements that hold food in a hot, dry atmosphere. They represent the bottom tier of holding cabinets.
Advantages:
- Ideal for quick service during busy periods.
- Minimal cleaning required.
- Simple operation.
- Lower cost compared to more advanced cabinets.
Disadvantages:
- Decreases hold times due to the dry atmosphere.
- Moisture evaporates from food, which decreases food quality.
- Heat rises, leading to temperature fluctuations.
- Utilize thermostats that require regular calibration and are only accurate within 10˚F.
Passive Humidified Holding Cabinets
Description: These cabinets feature an interior water bath to introduce humidity. However, the water temperature is not directly controlled, meaning the water vapor only indirectly affects food quality.
Passive Humidified Holding Cabinet Disadvantages:
- Significantly, small water bath limits humidity.
- Water is not heated separately. Consequently, this causes poor food temperature control.
- Significant hot and cold zones.
- Notably, most passive cabinets utilize a thermostat. These require calibration. Critically, thermostats are only accurate within 10˚F.

Advantages:
- Food holds in a hot, humid atmosphere, which facilitates quick service during busy periods.
- Increased humidity provides better hold time than dry cabinets.
- Lower cost than some more advanced cabinets.
- Provides better yields than dry cabinets.
- Simple operation.
Disadvantages:
- A small water bath limits humidity.
- Since the water is not heated separately, it causes poor food temperature control.
- Experiences significant hot and cold zones.
- Most utilize thermostats that require calibration and are only accurate within 10˚F.

Humidified Holding Cabinets
Description: Humidified cabinets are more advanced, featuring large water reservoirs that heat directly, rather than passively.
Advantages:
- Food holds hot, facilitating quick service during busy periods.
- The heated reservoir is adjustable, providing better control over food quality.
- Provides extended hold times.
- Generates good temperature stratification.
- Delivers better overall food quality than dry or passive cabinets.
- Increased yield.
Disadvantages:
- Water temperature may not be controlled precisely, meaning food temperature control is not exact.
- Humidity level is commonly adjusted by a 0-10 setting, which means water temperature isn’t controlled precisely.
- Insulated reservoirs can sometimes cause food temperatures to overshoot the desired setting.
- May utilize thermostats that require regular calibration and are only accurate within 10˚F.
- Settings are often determined by trial and error.
- Daily cleaning is recommended.
- Higher cost than dry or passive humidified cabinets.

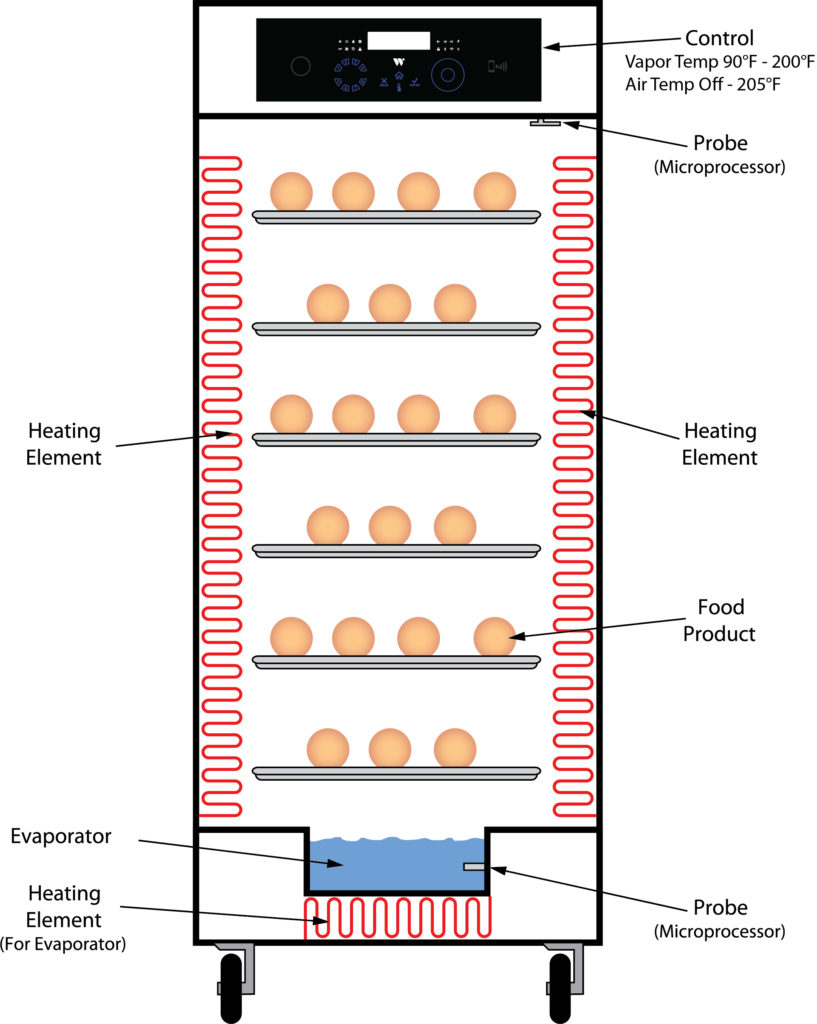
CVap® Controller Vapor Cabinets
Description: CVap is considered the “top dog” in holding cabinets. Unlike other humidified cabinets that rely solely on humidity for texture control (which often decreases food temperature and quality), CVap uses a dual-heat system. Vapor heat controls food temperature, while air heat controls food texture, allowing independent control of both.
Advantages:
- Food holds at the desired temperature for extended times, ideal for both busy and slow periods.
- Food temperature and texture are independently controlled.
- Eliminates hot and cold zones.
- Uses a microprocessor that eliminates calibration and is accurate to within 2˚F, providing superior temperature control.
- Offers the best overall food quality and longest holding times.
- Prevents food from drying out and maintains the food’s desired exterior.
- Ensures food remains above the temperature danger zone.
- Reduces food waste, thereby lowering food costs.
- Resolves key operational pain points such as long ticket times, poor food quality, employee skill gaps, high labor costs, and food safety/FDA compliance. CVap reduces ticket times, maintains food quality, simplifies operation (push-button simplicity), reduces labor needed, and is highly effective for HACCP temperature compliance by recording up to two years of data.
Disadvantages:
- The price is higher than some competitors due to its advanced capabilities.
- Some operators may not require its extended hold capabilities.
- Its appearance can sometimes cause confusion as it looks similar to some standard humidified cabinets.
- Daily cleaning is recommended.
FAQs
• What are the main types of food holding cabinets? There are three basic categories: dry, passive humidified, and humidified. CVap® cabinets are a specialized, advanced type of humidified cabinet.
• What is a “hot box”? “Hot box” is another term sometimes used for a dry cabinet, which is the most basic type of holding cabinet.
• Why do dry cabinets have shorter hold times compared to humidified ones? Dry cabinets operate in a hot, dry atmosphere, which causes moisture to evaporate from food, thereby decreasing hold times and food quality. Humidified cabinets, by contrast, introduce moisture to mitigate this.
• How does a passive humidified cabinet differ from a standard humidified cabinet? In passive humidified cabinets, the interior water bath’s temperature is not directly controlled, limiting its effect on food quality. In standard humidified cabinets, the large water reservoir is directly heated, allowing for better control.
• What makes CVap® cabinets unique in controlling food quality? CVap® cabinets use a dual-heat system, where vapor heat controls food temperature and air heat controls food texture independently. Other humidified cabinets often attempt texture control by merely decreasing humidity, which can negatively impact food temperature and overall quality.
• How accurate are the temperature controls in different cabinets? Thermostats used in dry, passive, and some humidified cabinets are generally accurate only within 10˚F and require regular calibration. CVap® cabinets, however, use a microprocessor that eliminates calibration and is accurate to within 2˚F.
• Which cabinet type offers the longest holding times and best food quality? CVap® holding cabinets offer the best overall food quality and longest holding times due to their precise independent control over food temperature and texture.
• Which holding cabinets require daily cleaning? Daily cleaning is recommended for both general humidified holding cabinets and CVap® holding cabinets.
Commercial Uses and Benefits
Holding cabinets, particularly advanced ones like CVap®, are designed to address various “pain points” for foodservice operations and are used across many commercial settings.
Key Commercial Benefits:
• Reduced Ticket Times: By holding food at optimal temperature and quality, CVap® cabinets significantly reduce the time needed to fulfill customer orders.
• Consistent Food Quality: These cabinets help maintain food’s intended quality, preventing degradation over time. This is especially true for CVap®, which independently controls temperature and texture.
• Improved Employee Efficiency: CVap® simplifies operation, allowing staff to manage food with “push-button simplicity,” which reduces the labor needed and the impact of under-skilled employees.
• Lower Labor Costs: By reducing staff requirements and simplifying operations, these cabinets can help restaurants lower labor expenses.
• Enhanced Food Safety & Compliance: CVap® is particularly effective for HACCP temperature compliance, as it keeps food above the temperature danger zone and can record up to two years of data for easy downloads.
• Reduced Food Waste and Costs: Extended hold times and better food quality directly translate to less food waste and lower overall food costs for businesses.
These cabinets are utilized in diverse commercial environments, from schools to chains, healthcare facilities, and fine dining establishments, wherever quality food service is essential.